Introduction
The Ultimate Guide to SD-WAN explores how this technology transforms modern business networks. As organizations move to cloud services, traditional WANs struggle to keep up with new demands. SD-WAN supports seamless connections to all types of cloud environments. This includes SaaS applications, private clouds, public clouds, and hybrid solutions. Traditional MPLS networks simply weren’t designed for these modern cloud connections. Most businesses can benefit from SD-WAN’s flexibility. However, some industries like Defense and Healthcare have special requirements that may limit adoption.
Key Advantages
SD-WAN offers key advantages for today’s connected businesses. First, it reduces network costs by allowing the use of multiple internet connections. Second, it improves application performance through smart routing decisions. The technology also simplifies network management, IT teams can control everything from a central dashboard. Furthermore, they can deploy new sites quickly with zero-touch provisioning.
Network Security at its Heart
Network security sits at the heart of SD-WAN design. Modern threats require multiple layers of protection, and SD-WAN delivers this through built-in security features. SD-WAN creates encrypted tunnels between all network locations. This ensures sensitive data remains protected as it travels across public internet connections.
Network segmentation plays a crucial role in limiting threat exposure. By dividing the network into separate zones, SD-WAN contains potential security breaches. Each zone operates independently with its own security policies. Micro-segmentation takes this protection further. It allows businesses to create security boundaries around individual applications or services. This means a compromised application can’t affect others on the network.
With built-in security features including application-aware firewalls and malware protection. SD-WAN can also automatically update security policies across all network locations. Most importantly, it responds quickly to emerging threats.
In this Ultimate Guide to SD-WAN we’ll be covering why this technology is important for today’s businesses, key terminology, the pro’s and con’s as well as some tips to remember in choosing an SD-WAN partner.
What is SD-WAN and why does it matter?
Modern businesses face growing demands on their networks as cloud applications, remote work, and digital operations expand. SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Networking) transforms how companies connect their offices, data centers, and cloud resources while reducing costs and complexity.
Traditional MPLS networks require private circuits and complex management. They were often designed around the 80%/20% principle, where 80% of the traffic stays local and 20% traverses the WAN backbone. With the rise of cloud-based SaaS applications, more and more traffic has to traverse the WAN to reach the internet, often resulting in poor application performance and frustrated employees. SD-WAN solves these challenges by intelligently routing traffic across multiple connection types, automatically selecting the best path for each application. For example, video conferencing traffic can take the fastest route while email uses a cheaper path.
Reduced Networking Costs
Companies implementing SD-WAN typically see 30-50% reduction in networking costs by replacing expensive MPLS connections with broadband internet. Branch offices can be deployed in days instead of months, accelerating business expansion. When retailers open new locations or manufacturers add production facilities, SD-WAN enables rapid, secure connectivity.
IT teams gain centralized control and visibility across the entire network through a single dashboard. Problems can be identified and fixed quickly, often before users notice issues. The built-in security features protect sensitive data as it moves between locations, while ensuring regulatory compliance.
For businesses focused on digital transformation, SD-WAN provides the agile, reliable, and cost-effective network foundation needed to support cloud applications, remote workers, and future growth.

Terms to Know
- An SD-WAN edge manages traffic and security through physical or virtual appliances at branch offices and data centers. It works as the foundation of Software-Defined Wide Area Networks.
- The SD-WAN controller orchestrates the entire network from a central location, typically operating from the cloud or data center. It actively manages policies and monitors all connected edge devices.
- Transport independence empowers organizations to combine different network links – MPLS, broadband internet, 4G/5G, and satellite connections. These create a hybrid WAN that uses multiple paths at once.
- Quality of Service (QoS) and application-aware routing direct traffic based on real-time conditions and application needs. The system measures latency, jitter, and packet loss to make smart routing choices.
- Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) configures new SD-WAN devices automatically when they connect to the network. It works with template-based provisioning to deploy standard configurations quickly across sites.
- The overlay network creates a virtual layer on top of the physical underlay infrastructure. This abstraction enables flexible network management, while VPNs connect locations securely.
- Policy-based routing follows rules to handle different types of traffic. Administrators create these policies based on applications, users, security needs, and business priorities.
- Network segmentation divides the network into secure zones. This approach contains security threats while maintaining proper access controls through micro-segmentation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SD-WAN
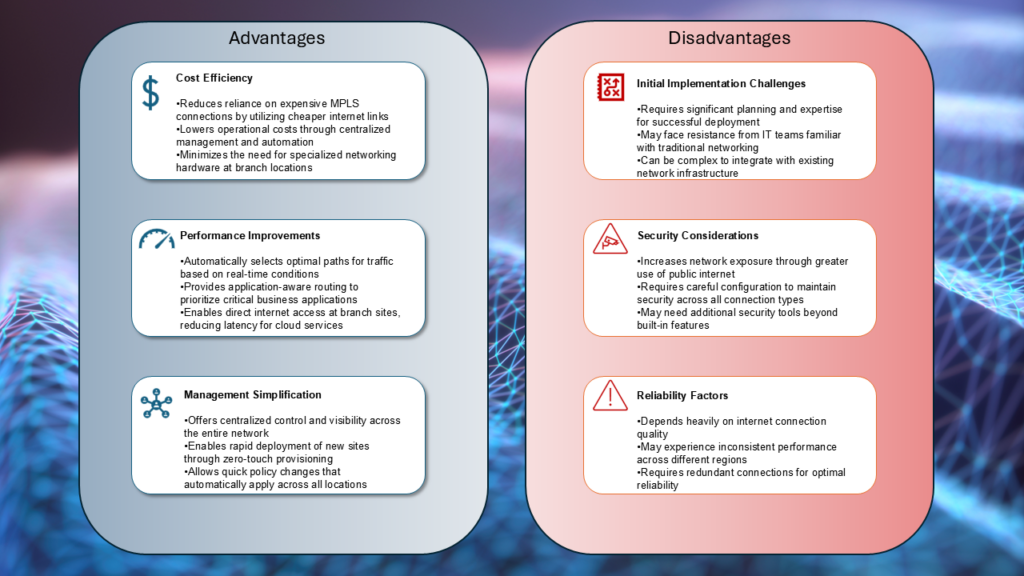
Advantages of SD-WAN:
- Cost Efficiency
-
Reduces reliance on expensive MPLS connections by utilising cheaper internet links
Lowers operational costs through centralised management and automation
Minimises the need for specialised networking hardware at branch locations - Performance Improvements
-
Automatically selects optimal path for traffic based on real-time conditions
Provides application-aware routing to prioritise critical business applications
Enables direct internet access at branch sites, reducing latency for cloud services - Management Simplification
-
Offers centralised control and visibility across the entire network
Enables rapid deployment of new sites through zero-touch provisioning
Allows quick policy changes that automatically apply across all locations
Disadvantages of SD-WAN:
- Initial Implementation Challenges
-
Requires significant planning and experience for successful deployment
May face resistance from IT teams familiar with traditional networking
Can be complex to integrate with existing network infrastructure - Security Considerations
-
Increases network exposure through greater use of public internet
Requires careful configuration to maintain security across all connection types
May need additional security tools beyond built-in features - Reliability Factors
-
Depends heavily on internet connection quality
May experience inconsistent performance across different regions
Requires redundant connections for optimal reliability
Top Tips for SD-WAN
- Partner with a Recognised Service Provider
-
A reputable provider brings expertise, proven deployment methods, and comprehensive support. They help overcome common challenges like security configuration, integration complexity, and performance optimisation. Their experience typically includes pre-tested solutions and established best-practices.
- Start with a Detailed Network Assessment
-
Your chosen Service Provider will be able to assist with this. Analyse your current traffic patterns, application requirements, and bandwidth needs before deployment. This helps identify critical applications and potential bottlenecks early. Document your existing infrastructure to plan for a smooth integration.
- Implement Strong QoS Policies
-
Create detailed Quality of Service policies that align with business priorities. Focus on critical applications first and ensure they receive appropriate bandwidth and priority. Review and adjust these policies regularly based on performance data.
- Plan for Redundancy
-
Deploy multiple connection types at each location for resilience. consider combining broadband, cellular and satellite connections. ensure automatic failover is properly configured and tested.
- Prioritise Security
-
From day one enable all security features before connecting to production networks. Implement network segmentation immediately and regularly review security policies. Consider integrating additional security, for example an SSE solution as part of an overarching SASE framework.
- Document Your Deployment Process
-
Create standardised procedures for new site deployments, or ensure your provider has these documented for you. Include configuration templates, testing protocols, and troubleshooting guides. This ensures consistent deployment across all locations.
- Monitor Performance Continuously
-
Depending on your service provider offering this may be something they offer. Use SD-WAN’s analytics capabilities to track network performance. Set up alerts for abnormal conditions and regularly review performance trends. This helps identify issues before they impact users.
- Train Your IT Team
-
Invest in training for your networking team to manage the SD-WAN effectively. Include both technical and operational aspects in the training. Keep the team updated on new features and best practices.
- Plan for Growth
-
Ensure your SD-WAN architecture is deigned with growth in mind. consider bandwidth scalability, additional sites, and new applications. Include cloud connectivity requirements in your planning.
- Regular Maintenance Schedules
-
Establish a routine for updates, security patches, and policy reviews. Keep firmware updated on all devices and regularly test disaster recovery procedures. Schedule periodic revies with your service provider to optimise performance
Resources for SD-WAN
In Closing
SD-WAN represents a significant evolution in network technology that addresses many traditional WAN limitations. Most importantly, it provides the agility and flexibility modern businesses need for their digital transformation journey.
Through intelligent traffic routing and application awareness, SD-WAN optimises network performance while reducing costs. Furthermore, its centralized management simplifies network operations, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance.
While implementing SD-WAN may seem daunting at first, partnering with an experienced service provider significantly smooths the transition. They bring valuable expertise in security configuration, deployment strategies, and ongoing optimization.
Future Focused
Looking ahead, SD-WAN continues to evolve with advancing technology. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services and remote work capabilities, the importance of flexible, secure networking grows. Additionally, the integration of AI and automation promises even more sophisticated network management capabilities.
Most critically, SD-WAN’s approach to security through network segmentation and encrypted communications provides a robust foundation for protecting business assets. By combining this security with improved performance and simplified management, SD-WAN delivers a networking solution that meets both current needs and future challenges.
In conclusion, SD-WAN offers a path to more efficient, secure, and adaptable networks that align with modern business requirements.
I hope this Ultimate guide to SD-WAN helped de-mystify this technology, enables you to move to SD-WAN or otherwise piqued your interest.





2 thoughts on “The Ultimate Guide to SD-WAN”
Comments are closed.