Introduction
As enterprises increasingly adopt Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN), business leaders need clear SD-WAN business metrics to evaluate return on investment and technology effectiveness. While IT teams focus on technical specifications, executives require metrics that demonstrate tangible business impact and organizational value. This post outlines the key performance indicators (KPIs) that leaders should monitor to assess SD-WAN success and effectively communicate value to stakeholders and board members.
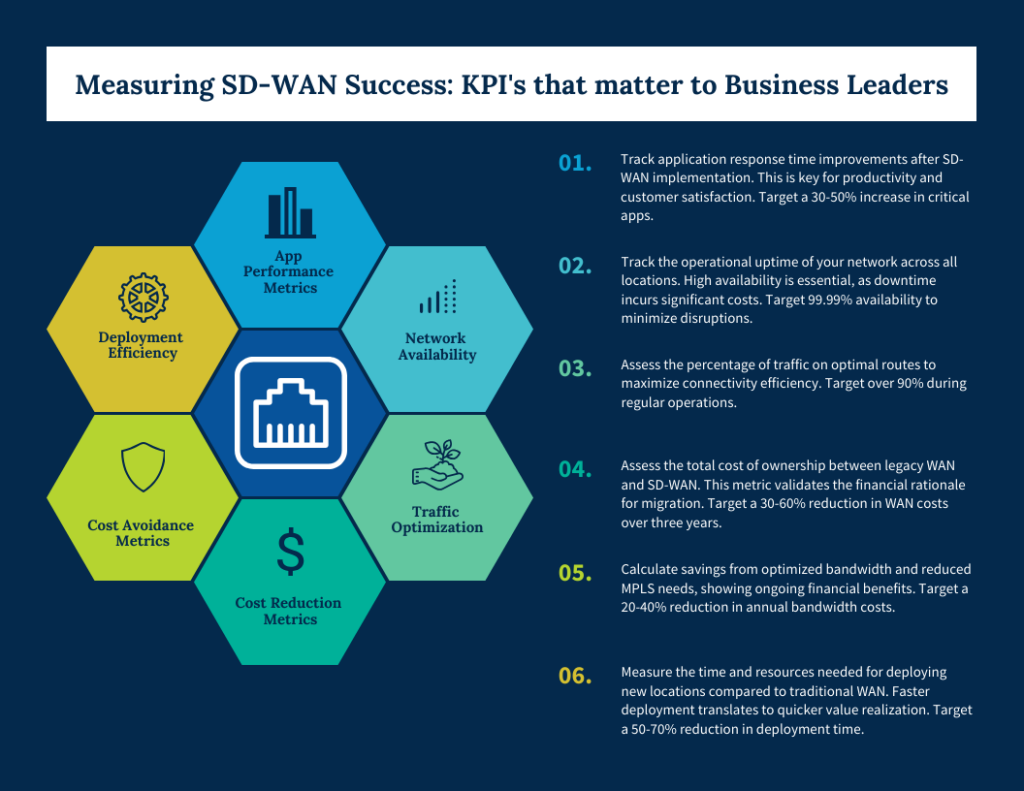
Network Performance Metrics
Establishing the right SD-WAN business metrics for network performance is crucial for quantifying technical improvements in business terms. The following three metrics provide executives with clear visibility into how SD-WAN enhances connectivity quality across the organization.
1. Application Performance Improvement
What to measure: Percentage improvement in application response times compared to pre-SD-WAN baseline.
Why it matters: Application performance directly impacts employee productivity and customer satisfaction. Slow applications create frustration, extend task completion times, and ultimately affect revenue generation. For customer-facing applications, even milliseconds of delay can influence conversion rates and customer retention.
Target: 30-50% improvement for critical applications.
Business impact: Proper implementation of SD-WAN business metrics for application performance enables leaders to quantify productivity gains. For example, a 30% improvement in ERP response time might translate to 45 minutes saved per employee per week, which across 500 employees represents significant operational efficiency. Additionally, faster customer-facing applications can improve conversion rates by 2-5%, directly affecting top-line revenue.
2. Network Availability
What to measure: Percentage of time the network is operational across all sites.
Why it matters: Every minute of downtime has quantifiable business costs. Network outages halt operations, prevent customer transactions, and damage brand reputation. Moreover, inconsistent availability creates unpredictable business operations and erodes confidence in digital transformation initiatives.
Target: 99.99% or higher availability (less than 52 minutes of downtime per year).
Business impact: When evaluating SD-WAN business metrics, availability should be converted to financial terms. For instance, if an hour of downtime costs $50,000 in lost productivity and transactions, improving availability from 99.9% to 99.99% represents approximately $350,000 in annual cost avoidance. Furthermore, higher availability enables business leaders to confidently migrate more critical applications to the cloud, accelerating digital transformation.
3. Traffic Optimization
What to measure: Percentage of traffic routed through optimal paths versus backup paths.
Why it matters: Optimal traffic routing ensures maximum value from connectivity investments. Traditional WANs often underutilize available bandwidth due to static configurations, while SD-WAN dynamically routes traffic based on current network conditions and application requirements.
Target: 90%+ of traffic using optimal paths during normal operations.
Business impact: Effective SD-WAN business metrics for traffic optimization reveal both cost savings and performance improvements. By increasing optimal path utilization from 70% to 90%, organizations can postpone bandwidth upgrades, saving 15-25% on annual connectivity costs. Additionally, intelligent traffic routing enables businesses to prioritize mission-critical applications during network congestion, maintaining performance for revenue-generating activities even under suboptimal conditions.
Financial Metrics
Tracking financial SD-WAN business metrics is essential for justifying the initial investment and demonstrating ongoing value to C-suite executives. The following financial KPIs translate technical improvements into the language of business leadership.
1. Cost Reduction
What to measure: Total cost of ownership (TCO) comparison between legacy WAN and SD-WAN.
Why it matters: Cost reduction is typically the primary justification for SD-WAN implementation. Traditional MPLS-based networks often incur high operational expenses and bandwidth costs, while SD-WAN leverages more affordable internet connections without sacrificing performance. Therefore, comprehensive cost analysis validates the initial business case and provides evidence of successful implementation.
Target: 30-60% reduction in WAN costs over 3 years.
Business impact: Properly documented SD-WAN business metrics for cost reduction provide finance leaders with clear ROI evidence. For example, a mid-sized enterprise with 50 locations might reduce annual network expenses from $1.2 million to $600,000, resulting in $1.8 million savings over three years. Additionally, these savings can be reallocated to other strategic IT initiatives, creating a compounding positive impact on digital transformation efforts.
2. Cost Avoidance
What to measure: Expenses avoided through optimized bandwidth usage and reduced need for MPLS circuits.
Why it matters: Beyond direct cost reductions, SD-WAN implementations frequently delay or eliminate the need for bandwidth upgrades as business requirements grow. Moreover, the ability to seamlessly incorporate consumer-grade internet connections alongside premium circuits creates ongoing cost avoidance that might not appear in direct cost comparisons.
Target: 20-40% reduction in annual bandwidth costs.
Business impact: Forward-looking SD-WAN business metrics should account for avoided costs over a 3-5 year horizon. For instance, a company that would have needed to increase MPLS capacity by 50% to support growing cloud usage can instead leverage SD-WAN’s traffic optimization capabilities with existing connections. Furthermore, when new offices open, using primarily broadband internet rather than MPLS can reduce per-site connectivity costs by 60-70%, significantly improving expansion economics.
3. Deployment Efficiency
What to measure: Time and resources required to deploy new locations compared to traditional WAN.
Why it matters: Traditional WAN deployments often require specialized on-site expertise and can take weeks or months per location. In contrast, SD-WAN solutions typically feature zero-touch provisioning and centralized management. Consequently, new sites can be brought online much faster, accelerating business initiatives and reducing deployment costs.
Target: 50-70% reduction in deployment time.
Business impact: When calculating comprehensive SD-WAN business metrics, deployment efficiency directly affects time-to-revenue for new locations. For example, reducing branch deployment time from 30 days to 10 days means new retail locations can begin generating revenue 20 days sooner. Additionally, simplified deployment reduces IT labour requirements by 30-50%, allowing technical resources to focus on more strategic initiatives rather than routine configuration tasks.

User Experience Metrics
Incorporating user-centric SD-WAN business metrics ensures that technical improvements translate to actual workforce productivity and satisfaction. These human-focused KPIs help bridge the gap between network performance statistics and real business outcomes.
1. End-User Satisfaction
What to measure: Survey-based metrics on user satisfaction with application performance.
Why it matters: Technical performance metrics often fail to capture the actual employee experience. Users may perceive issues that network monitoring tools miss, or conversely, may not notice technical improvements unless they significantly impact daily workflows. Therefore, collecting direct feedback through surveys provides a reality check for technical KPIs and highlights areas needing attention.
Target: 85%+ satisfaction rate.
Business impact: Regular assessment of SD-WAN business metrics related to user satisfaction helps quantify employee experience improvements. For instance, increasing satisfaction scores from 65% to 85% often correlates with reduced shadow IT implementations, as employees no longer feel compelled to circumvent corporate systems. Additionally, higher satisfaction typically reduces employee frustration and improves retention, particularly for remote workers whose productivity depends entirely on network performance.
2. Support Ticket Reduction
What to measure: Percentage decrease in network-related support tickets.
Why it matters: Support tickets represent both visible problems and hidden costs. Each ticket not only indicates user frustration but also consumes IT resources for troubleshooting and resolution. Moreover, network-related tickets often represent productivity losses as employees wait for issues to be resolved.
Target: 40-60% reduction in network-related tickets.
Business impact: Support ticket metrics serve as leading indicators in SD-WAN business metrics frameworks. For example, reducing monthly network-related tickets from 500 to 200 can free up approximately 150 IT staff hours per month, representing $15,000 in labor cost reallocation. Furthermore, if each ticket previously represented an average of 30 minutes of lost productivity for affected employees, this reduction prevents approximately 9,000 hours of annual productivity loss across the organization.
3. SaaS Application Performance
What to measure: Response times for critical cloud applications (Office 365, Salesforce, etc.).
Why it matters: Cloud applications now form the backbone of most business operations. However, traditional WANs often route cloud traffic inefficiently through central data centres rather than directly to cloud providers. SD-WAN enables local internet breakout and optimized cloud connectivity, dramatically improving SaaS performance.
Target: 25-40% improvement in SaaS application performance.
Business impact: Cloud application performance stands as one of the most immediately noticeable SD-WAN business metrics. For example, reducing Salesforce page load times from 5 seconds to 3 seconds might enable sales representatives to complete 15% more customer records daily. Additionally, improved Microsoft Teams or Zoom performance during video conferences eliminates communication barriers between offices, enhancing collaboration and decision-making speed. Consequently, these improvements often translate to measurable productivity gains in departments heavily reliant on cloud services.
Business Continuity Metrics
Resilience-focused SD-WAN business metrics quantify an organization’s ability to maintain operations during disruptions. These KPIs are particularly valuable for executives concerned with operational risk management and business continuity planning.
1. Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR)
What to measure: Average time required to restore service after an outage.
Why it matters: Network disruptions are inevitable, but their business impact varies dramatically based on recovery speed. Traditional WANs often require manual intervention and physical presence to restore service. In contrast, SD-WAN’s automated failover capabilities and centralized management significantly reduce recovery times. Therefore, MTTR directly correlates with financial impact of outages.
Target: 50-70% reduction in recovery time.
Business impact: MTTR reduction represents one of the most financially significant SD-WAN business metrics. For instance, reducing average recovery time from 4 hours to 1 hour for a critical manufacturing location could prevent $150,000 in lost production per incident. Moreover, faster recovery maintains customer service levels during disruptions, protecting brand reputation and preventing customer churn. Additionally, predictable recovery times enable more accurate business continuity planning and risk assessment.
2. Failover Success Rate
What to measure: Percentage of successful automatic transitions to backup connections.
Why it matters: Automatic failover is a key SD-WAN benefit, but its reliability determines actual business value. Failed failovers create extended outages despite redundant connections. Furthermore, inconsistent failover performance undermines confidence in business continuity plans and creates unpredictable operational risks.
Target: 99%+ successful failover rate.
Business impact: Failover reliability serves as a critical component in comprehensive SD-WAN business metrics frameworks. For example, improving failover success from 90% to 99% means that for every 100 connectivity issues, 9 fewer will require manual IT intervention. Additionally, reliable failovers enable businesses to operate with leaner IT teams, as after-hours support requirements decrease substantially. Consequently, organizations can reduce overtime costs and improve IT staff retention by minimizing emergency response situations.
3. Disaster Recovery Readiness
What to measure: Time required to activate disaster recovery configurations.
Why it matters: Major disasters require network reconfiguration to support relocated operations or alternative work arrangements. Traditional WANs often require extensive manual reconfiguration during disasters, delaying recovery. SD-WAN’s centralized policy management enables rapid adaptation to emergency situations.
Target: 80%+ reduction in disaster recovery activation time.
Business impact: Disaster recovery metrics complete the resilience portion of SD-WAN business metrics. For instance, reducing network reconfiguration time from 24 hours to 4 hours during a site evacuation could save millions in lost productivity and revenue. Furthermore, faster recovery capabilities may reduce business interruption insurance premiums by demonstrating enhanced resilience. Additionally, improved disaster recovery metrics often satisfy regulatory requirements for critical industries, reducing compliance risks and potential penalties.
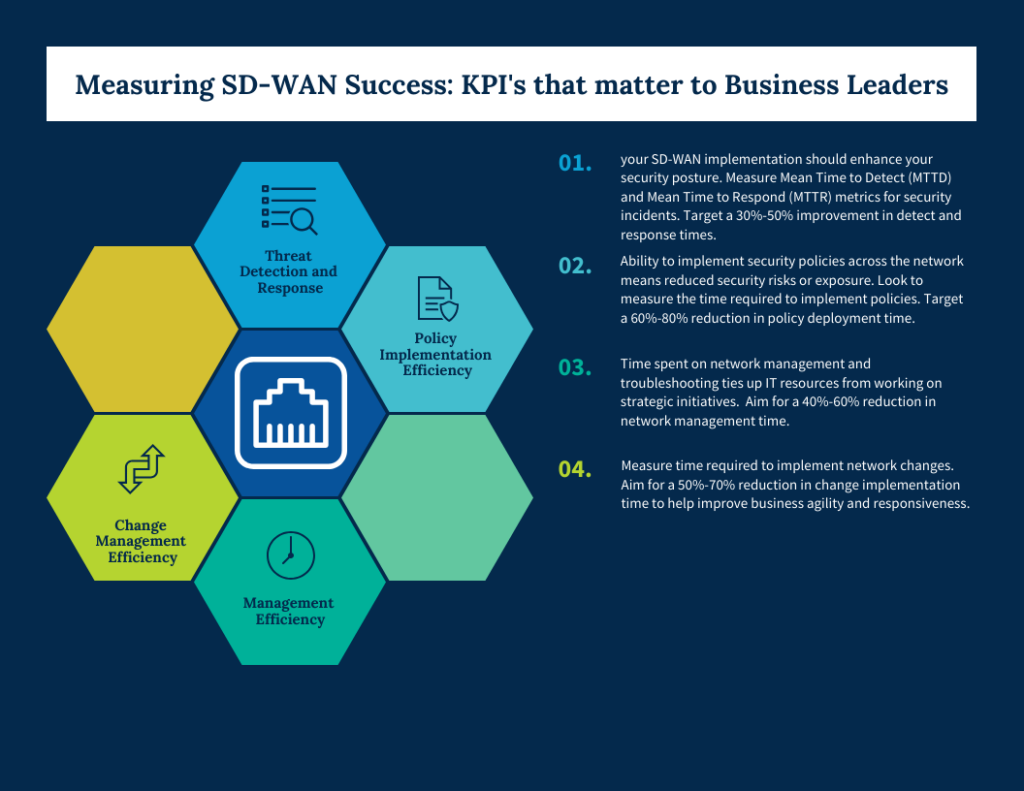
Security Metrics
Cybersecurity-focused SD-WAN business metrics enable executives to quantify risk reduction and compliance improvements. These security KPIs translate technical protections into business risk management language that resonates with executive leadership.
1. Threat Detection and Response
What to measure: Mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR) to security incidents.
Why it matters: Network security breaches can cause devastating financial and reputational damage. Traditional WANs often rely on perimeter security at centralized locations, creating blind spots at branch offices. Conversely, SD-WAN typically integrates security functions directly into the network fabric, enabling faster detection and response to threats. Therefore, these metrics directly correlate with an organization’s security posture and risk exposure.
Target: 30-50% improvement in detection and response times.
Business impact: Security incident timing represents a critical component of SD-WAN business metrics. For example, reducing threat detection time from 9 hours to 4 hours significantly limits potential damage from breaches, potentially saving millions in remediation costs. Additionally, faster threat response minimizes data exfiltration opportunities and reduces regulatory reporting requirements in many jurisdictions. Furthermore, improved security metrics often translate to more favourable cyber insurance premiums, creating ongoing cost benefits beyond the direct security improvements.
2. Policy Implementation Efficiency
What to measure: Time required to implement new security policies across the network.
Why it matters: Emerging threats require rapid security responses across the entire network. Traditional WANs often require device-by-device configuration changes, creating significant delays in implementing critical security updates. Moreover, this approach increases the risk of configuration errors that could create new vulnerabilities. SD-WAN enables centralized policy management with consistent deployment across all locations.
Target: 60-80% reduction in policy deployment time.
Business impact: Policy implementation efficiency stands as a forward-looking SD-WAN business metric that quantifies security agility. For instance, reducing security policy deployment time from days to hours enables organizations to respond to zero-day vulnerabilities before they can be widely exploited. Additionally, consistent policy implementation reduces configuration errors that might create security gaps. Consequently, organizations can maintain stronger compliance postures with less effort, reducing both security risks and audit findings that might otherwise require expensive remediation.
Operational Metrics
1. Management Efficiency
Operational SD-WAN business metrics quantify improvements in IT team efficiency and organizational agility. These KPIs demonstrate how SD-WAN transforms IT from a cost centre to a business enabler through improved operational capabilities.
What to measure: Time spent on network management and troubleshooting.
Why it matters: IT teams historically spend significant time on routine network maintenance and troubleshooting rather than strategic initiatives. Traditional WANs require device-level management across geographically distributed locations, creating substantial operational overhead. In contrast, SD-WAN’s centralized management and automated operations dramatically reduce maintenance requirements, freeing IT resources.
Target: 40-60% reduction in network management time.
Business impact: Management efficiency serves as a foundational component of SD-WAN business metrics. For example, reducing network management time from 120 hours to 50 hours monthly enables IT staff reallocation worth $100,000+ annually for a mid-sized organization. Additionally, reduced management overhead enables faster response to business needs rather than focusing on “keeping the lights on.” Furthermore, improved operational efficiency often enables organizations to expand network capabilities without corresponding increases in IT headcount, improving the scalability of business operations.
2. Change Management Efficiency
What to measure: Time required to implement network changes.
Why it matters: Business agility increasingly depends on network agility. Traditional WANs create bottlenecks for business initiatives due to complex, time-consuming change processes. Moreover, fear of disruption often leads to change freezes that further delay innovation. SD-WAN’s automation and centralized orchestration enable rapid, consistent change implementation with reduced risk.
Target: 50-70% reduction in change implementation time.
Business impact: Change velocity represents one of the most transformative SD-WAN business metrics. For instance, reducing application deployment time from weeks to days accelerates time-to-market for new digital initiatives, creating competitive advantages. Additionally, faster network changes support more rapid business expansion, acquisition integration, and workload migration. Consequently, improved change efficiency transforms networking from a business constraint to a business enabler, supporting organizational innovation rather than restricting it.
Implementation Roadmap: Turning Strategy into Measurable Success
Implementing SD-WAN is more than a technical deployment—it’s a business transformation initiative that requires strategic planning and careful measurement. A structured approach ensures that your investment delivers tangible value aligned with your business objectives.
1. Establish Baselines
Before your SD-WAN implementation begins, document your current network performance metrics. This critical first step creates a foundation for measuring improvement and demonstrating ROI. Consider capturing:
- Current application performance data across all locations
- Existing bandwidth costs and utilization rates
- Network reliability metrics including outage frequency and duration
- Mean time to repair (MTTR) for network issues
- IT staff time allocation for network management tasks
2. Set Targets
With baselines established, define specific, measurable goals that align with business priorities. Effective targets should:
- Reflect industry benchmarks while accounting for your unique business context
- Balance technical performance with business outcomes
- Include both short-term wins and long-term strategic objectives
- Be ambitious yet achievable to maintain stakeholder confidence
- Incorporate input from business units beyond IT to ensure alignment
3. Implement Monitoring
Deploy comprehensive monitoring solutions that capture both technical and business-focused metrics. Your monitoring approach should:
- Integrate with existing business intelligence platforms
- Provide real-time visibility through intuitive dashboards
- Enable drill-down capabilities for troubleshooting
- Support automated alerts for performance thresholds
- Include end-user experience monitoring to capture the actual business impact
4. Regular Review
Establish a cadence of quarterly performance reviews with key stakeholders. These sessions should:
- Compare current performance against baselines and targets
- Identify emerging trends before they impact business operations
- Analyze correlations between network improvements and business outcomes
- Adjust expectations and targets based on changing business priorities
- Document success stories and quantified benefits for executive reporting
5. Continuous Improvement
Transform performance data into actionable insights that drive ongoing optimization:
- Fine-tune SD-WAN policies based on application usage patterns
- Adjust bandwidth allocations to match evolving business needs
- Identify opportunities to consolidate or eliminate redundant services
- Collaborate with application owners to optimize critical workflows
- Develop best practices for future network expansions or application deployments
By following this structured implementation roadmap, organizations can ensure their SD-WAN investments deliver measurable business value while maintaining the agility to adapt to changing market conditions and business requirements.

Conclusion
Measuring SD-WAN success requires a balanced approach that considers technical performance, financial outcomes, and business impact. By focusing on these key performance indicators, business leaders can ensure their SD-WAN investments deliver measurable value to the organization. More importantly, these metrics provide a common language for IT and business stakeholders to discuss network performance in terms of business outcomes rather than technical specifications.
Remember that the most relevant KPIs will vary based on your organization’s specific goals for SD-WAN implementation. Prioritize metrics that align with your primary business objectives, whether that’s cost reduction, improved application performance, enhanced security, or greater business agility.


